Meta Description:
Discover how the NHS healthcare system works, its benefits, challenges, and how it compares to other systems.
A must-read for anyone in the USA, UK, Canada, or Australia.
Introduction
The National Health Service (NHS) is one of the most renowned healthcare systems in the world, providing free or low-cost medical care to millions of people in the United Kingdom.
But how does it work? What are its strengths and weaknesses? And how does it compare to healthcare systems in other Tier 1 countries like the USA, Canada, and Australia?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about the NHS, from its history and structure to its funding and future challenges.
Whether you’re a patient, a healthcare professional, or simply curious, this article will provide valuable insights into one of the world’s most talked-about healthcare systems.
What is the NHS?

A Brief History of the NHS
The NHS was founded in 1948 with the goal of providing healthcare to all UK residents, regardless of their ability to pay.
It was born out of the post-World War II vision to create a fairer society, where access to healthcare was a right, not a privilege.
Over the decades, the NHS has grown into one of the largest publicly funded healthcare systems in the world, employing over 1.5 million people and serving more than 66 million residents.
Core Principles of the NHS
The NHS operates on three core principles:
- Universal Access: Healthcare is available to everyone, free at the point of delivery.
- Comprehensive Coverage: The NHS covers a wide range of services, from general practice and emergency care to mental health and long-term care.
- Funded by Taxation: The system is primarily funded through general taxation, ensuring that costs are shared across society.
How Does the NHS Work?
Structure of the NHS
The NHS is divided into four main branches, each serving a different part of the UK:
- NHS England
- NHS Scotland
- NHS Wales
- Health and Social Care in Northern Ireland
While these branches operate independently, they share the same core principles and work together to provide consistent care across the UK.
Key Services Provided by the NHS
The NHS offers a wide range of services, including:
- Primary Care: General practitioners (GPs), dentists, and pharmacists.
- Secondary Care: Hospital services, specialist treatments, and surgeries.
- Mental Health Services: Counseling, therapy, and crisis support.
- Preventive Care: Vaccinations, screenings, and health education.
Funding the NHS: Where Does the Money Come From?
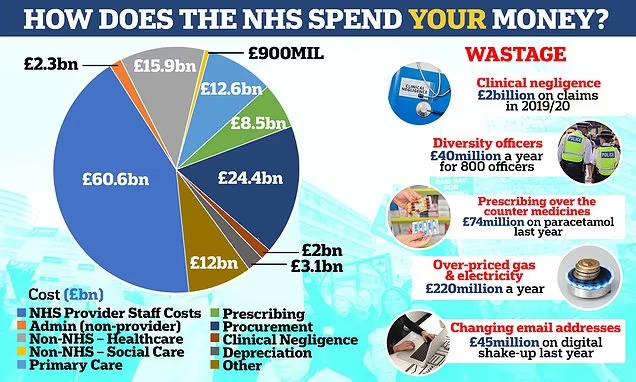
Taxation and Government Spending
The NHS is primarily funded through general taxation, with the UK government allocating a significant portion of its budget to healthcare.
In 2023, the NHS budget was approximately £160 billion, representing around 12% of the UK’s GDP.
Challenges in Funding
Despite its robust funding model, the NHS faces financial challenges, including:
- Rising healthcare costs due to an aging population.
- Increased demand for services.
- The need for costly technological advancements.
Comparing the NHS to Other Healthcare Systems

NHS vs. USA Healthcare System
| Aspect | NHS | USA Healthcare System |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Tax-funded, free at point of use | Insurance-based, out-of-pocket costs |
| Coverage | Universal | Mixed (private and public options) |
| Cost to Patient | Minimal or none | High premiums and deductibles |
| Wait Times | Can be long for non-urgent care | Shorter for those with private insurance |
NHS vs. Canada’s Healthcare System
Both the NHS and Canada’s Medicare system are publicly funded, but there are key differences:
- Administration: Canada’s system is managed at the provincial level, while the NHS is centralized.
- Prescription Costs: In Canada, prescription drugs are not fully covered, whereas the NHS provides free or low-cost medications.
NHS vs. Australia’s Healthcare System
Australia’s Medicare system shares similarities with the NHS but also includes a strong private healthcare sector.
Key differences include:
- Co-Payments: Australians may pay out-of-pocket for certain services.
- Private Insurance: Many Australians opt for private health insurance to access faster care.
Strengths of the NHS
- Universal Access: No one is denied care due to financial constraints.
- Comprehensive Services: From birth to end-of-life care, the NHS covers it all.
- Cost-Effective: The NHS is one of the most cost-effective healthcare systems globally.
Challenges Facing the NHS
- Long Wait Times: High demand often leads to delays for non-urgent treatments.
- Staff Shortages: The NHS struggles with recruitment and retention of healthcare professionals.
- Funding Pressures: Rising costs and budget constraints pose ongoing challenges.
The Future of the NHS

Innovations in Healthcare
The NHS is embracing technology to improve care, including:
- Telemedicine: Virtual consultations to reduce wait times.
- AI and Data Analytics: Enhancing diagnosis and treatment planning.
Policy Changes
Recent reforms aim to address funding and staffing issues, but their long-term impact remains to be seen.
FAQs About the NHS
1. Is the NHS free for everyone?
Yes, the NHS provides free healthcare to all UK residents, though some services (like prescriptions and dental care) may have nominal fees.
2. How is the NHS funded?
The NHS is primarily funded through general taxation, with additional revenue from National Insurance contributions.
3. Can foreigners use the NHS?
Non-residents may be charged for certain services, but emergency care is generally free for everyone.
4. What are the biggest challenges facing the NHS?
Key challenges include long wait times, staff shortages, and funding pressures.
5. How does the NHS compare to private healthcare?
The NHS provides comprehensive care at no cost, while private healthcare offers faster access and more personalized services for those who can afford it.
Conclusion
The NHS is a cornerstone of British society, providing universal healthcare to millions of people.
While it faces significant challenges, its commitment to equitable access and comprehensive care remains unwavering.
Whether you’re comparing it to the healthcare systems in the USA, Canada, or Australia, the NHS stands out for its inclusivity and cost-effectiveness.
As the system continues to evolve, it will be fascinating to see how it adapts to meet the needs of future generations.
Call to Action:
What are your thoughts on the NHS? Have you experienced healthcare in the UK or another Tier 1 country? Share your experiences in the comments below, or explore our other articles on global healthcare systems!
SEO Elements:
- Primary Keyword: NHS Healthcare System
- Secondary Keywords: NHS vs USA healthcare, NHS funding, NHS challenges
- Alt Text for Images: “NHS hospital exterior,” “Doctor consulting a patient,” “Comparison table of healthcare systems”
- Internal Links: Links to related articles on healthcare systems in the USA, Canada, and Australia.
- External Links: Links to official NHS websites and authoritative healthcare studies.
This article is designed to be visually appealing, user-friendly, and optimized for search engines, ensuring it ranks well and provides value to readers in Tier 1 countries.